%20in%20the%20hands%20of%20a%20doctor.jpg)
Worms are parasitic worms that live in the body of humans and animals. They are difficult to spot because, like many other diseases and conditions, they camouflage themselves. The symptoms of a helminth infestation range from mild malaise to fainting with severe poisoning. We'll tell you where you can get worms and how to get rid of them.
What's this
Worms are considered to be the most common parasites in humans. Today science knows about 300 worm diseases. The most common are intestinal worm diseases - enterobiasis and ascariasis, which affects more than 2 billion people.
The size of the worms living in the body varies from a few millimeters to several meters. For example, the length of pinworms that cause enterobiasis does not exceed 1 cm, some tapeworms (for example, the wide tapeworm) reach 12-15 meters.
Causes of Helminthiasis
Helminthiasis is a disease in which infection with worms occurs. Worms invade the human body and stay there. These parasites not only live in the intestines, but also in other organs and tissues.
According to the World Health Organization, every fourth person on earth is infected with worms. At the same time, WHO experts note that the actual number of people infected is at least 50%. This mainly affects countries with a poor hygiene culture (these are some countries in Africa and Southeast Asia). In other countries, more than 1. 5 million cases of helminth infections are recorded annually. Most of them are children.
How can you get infected with worms?
There are 4 routes of infection:
- Through the ground. Such diseases are called geohelminthiasis. Unwashed fruits can harbor tens of thousands of parasites. This is why it is so important to wash vegetables, fruits, and hands thoroughly before eating. Running pets are another source of soil parasites.
- Upon contact with an infected person. Parasitic worms are incredibly productive. The female pinworm can lay up to 5, 000 eggs in the human body in just one day. Eggs and adults can be passed on to other people through bedding and other household items. After that, it is enough for the infected not to wash their hands, and the worms will invade.
- When eating contaminated food. Such helminthic diseases are called biohelminthiasis. You can catch the parasite with insufficient heat treatment of meat, poultry or fish.
- From an insect bite. This type of transmission is rare. Very small parasites can usually be transmitted through insect bites.
Consider the risk factors that increase the likelihood of worm infection in adults and children:
- Disregarding hygiene rules - if you do not wash your hands after walking on the street, using the toilet or before eating.
- The habit of biting nails - under them there is a lot of dirt with microbes and parasites. This includes the habit of putting pens, pencils, and other objects in your mouth.
- Poor animal care, especially for those who go outside.
- Eat unwashed vegetables and fruits.
- Use water from questionable sources.
- Bad cleaning of the living spaces.
- Passion for animal feed that has not been properly processed in culinary terms.
Who is at risk

Nobody is immune to worm infection. It is enough to let up on hygiene and the parasite larva can "break through" into the body. The following groups of people are particularly susceptible to helminthiasis:
- Small children. Most often, helminthic invasions are found in children. This is because the child neglects the rules of hygiene. Small children put things in their mouths and they often dig in the mud in the streets. In groups, children tend to come into closer contact with one another than adults, which also increases the likelihood of infection.
- Families with pets. Eggs and larvae of parasites that got into living quarters from the street with pets can be anywhere. Owners of dogs, cats, and other animals are often unaware of the problem and learn of the presence of worms for a different reason when they contact a veterinarian.
- Gourmet. Lovers of exotic cuisine such as sushi, raw meat or fish are also at risk.
- Traveler. This is especially true for people traveling to countries with poor sanitation.
- Summer residents, farm workers. People who work in vegetable gardens, orchards or simply live in the country.
- People who come across raw fish or meat at work. For example, salespeople or cooks - when processing, cutting and preparing food.
Myth 1: There are no parasites in marine fish.
Many people mistakenly believe that worms are only found in river fish and that they are not in the sea because of the salt water. In fact, sea fish are mainly infested with parasites that are harmless to humans. In this regard, raw river fish is more dangerous than raw sea fish. But this does not mean that the sea fish is completely safe: it is always recommended to process any fish - thoroughly fry, boil or freeze for 3 days.
Classification of helminthiasis
There are several classifications of parasitic worms. According to localization, worms are:
- Gut - live in the small or large intestine. These include ascaris, eels, whipworms, beef tapeworms, and others.
- Lungs - live in the tissues of the bronchopulmonary system. Most of the time it is a lung fluke.
- Tissues - parasitizes on various tissues in the body. Tissue worms include Schistosomes, Trichinella, and Toxocar.
- Parasites of the liver and gallbladder. They are liver fluke, giant hepatic leech, and clonorch (Chinese leech).
Depending on the pathogen, there are 4 classes of helminth diseases:
- Nematodes - caused by roundworms. These are ascariasis, enterobiasis, trichinosis, trichocephalosis, toxocariasis, ankylostomiasis, and others.
- Cestodoses - the pathogens are tapeworms. Such pathologies include hymenolepiasis, teniasis, teniarinchiasis, diphyllobothriasis, and cystcercosis.
- Dystomyases are diseases caused by flatworms. These are fascioliasis, opisthorchiasis, dicroceliosis.
- Protozoses - The pathogens are protozoa such as lamblia, toxoplasma or amoeba.
More than 70 types of parasitic worms are common. The most common are the following helminthic diseases (see table).
| illness | The pathogen and its properties | Transfer method |
|---|---|---|
| Ascariasis | Called Ascaris. These are roundworms that live in the intestines. They can grow up to 30-40 cm tall, roundworms feed on almost all nutrients from food. During vital activity, worms injure the intestinal walls or even perforate them | Most commonly, Ascaris eggs are transmitted by the fecal-oral route. They stay in the ground and on the surface of vegetables, fruits, herbs and berries for a long time |
| Enterobiasis | It develops when pinworms enter the body. These are small round worms, 0. 5 to 1 cm in size. The main danger with enterobiasis is toxic waste products from worms | Contact with an infected person. Pinworm eggs stay on various surfaces for some time. |
| Giardiasis | Caused by microscopic parasites - lamblia. Pathogens produce toxic substances and injure tissues | Giardia is transmitted fecal-orally and through contaminated food and water |
| Opisthorchiasis | Pathogens are small worms up to 2 cm in size that most commonly parasitize the liver and bile ducts. With opisthorchiasis, poisoning with toxic substances and mechanical tissue damage occurs | Opisthorchiasis pathogens are transmitted through raw fish |
| Echinococcosis | It is caused by echinococci - tapeworms that do not exceed 5 cm in size. Echinococci parasitize on various tissues, including the heart and brain. Pathogens cause serious dysfunction of organs and body systems. In some cases, they can provoke a malignant tumor process. | They are spread through dirty hands and contaminated food. Echinococcus carriers can also be dogs and rodents. |
| Diphyllobothriasis | Pathogen - large tapeworms that reach 10-15 meters. Tapeworms live in the small intestine and cause severe damage to the host's body. Worms produce toxic substances and significantly impair the functioning of the digestive tract | Transmission through eating raw fish |
| Trichocephalosis | Called by whipworm, a round worm that looks like a hair. Vlasoglava can reach 5-6 meters. Worms live in the intestines and invade the submucosa. Cause poisoning, inflammation and acute anemia | Invasion occurs by swallowing the parasite's eggs |
The worm infestation is also divided into stages:
- Acute helminthiasis - appear 2-4 weeks after infection. In this case, the symptoms of worms are observed from 1 week to several months. If you do not do therapy, the disease becomes chronic.
- Chronic helminthiasis - manifestations depend on the type of parasite. If, for example, it is a question of parasites with larval reproduction, prolonged allergic reactions follow. Other chronic worm diseases may be asymptomatic or accompanied by pain, discomfort, fatigue, and other symptoms.
Complications of helminthiasis
If left untreated, helminthiasis leads to serious, sometimes life-threatening, complications:
- Anemia - anemia, insufficient numbers of red blood cells and hemoglobin in the blood. This condition is due to the fact that the worms use up some of the nutrients necessary for normal haematopoietic function.
- Destruction of tissues and organs. Worms live not only in the lumen of the gastrointestinal tract, but also in the thickness of tissues, for example, the liver, lungs, muscles. Tissues in particular are affected by worms during migration, when they migrate from one department (or organ) to another - ulcers and constant foci of inflammation develop. Against this background, the risk of developing infections and malignant tumors increases.
- Nervous system disorders. This is due to the toxic waste products from worms that poison the body. Nerve tissue is most sensitive to toxins. This can lead to irritability, headaches, insomnia, and other signs of nervous system damage.
- Allergic reaction. Toxins secreted by worms can also act as allergens. Human immunity can inadequately respond to these substances. This leads to the appearance of typical allergy symptoms - rashes, reddening of the skin, itching, and sometimes nausea and vomiting.

The presence of worms in the body also leads to a lack of the following minerals:
- Zinc. With zinc deficiency, immunity decreases, a person often catches colds and suffers from other infectious diseases. The likelihood of developing prostatitis and infertility increases because this trace element is extremely important for reproductive health.
- Selenium. Decreases immunity and also increases the risk of malignant tumors.
- Iodine. Iodine deficiency in children leads to growth and development disorders (physical and mental). In adults, the work of the thyroid gland deteriorates, metabolic processes slow down.
- Manganese. If there is a lack of manganese, the bones become brittle. A person loses weight quickly, he is often plagued by convulsions and dermatitis.
- Chrome. A deficiency in this element leads to development delays and impaired carbohydrate metabolism.
Worms and immunity
Often, worms are accompanied by other parasites - toxoplasma and chlamydia. This is due to the suppression of immunity. A healthy body can withstand intruders, but with helminthiasis, protection is weakened. Toxoplasmosis is particularly dangerous during pregnancy as it can lead to fetal death.
Symptoms of helminthiasis
Signs of worms are different in both adults and children. The most common symptoms are:
- Itching in the anus is the most common symptom of intestinal worms;
- Grinding of teeth in a dream - occurs due to toxins released by worms;
- drooling in sleep and in the morning;
- nausea when brushing your teeth in the morning;
- Peeling the skin of the hands and feet;
- allergic rashes;
- strong feeling of hunger up to fainting;
- Swelling (often allergic);
- itchy skin;
- chronic fatigue;
- Headache and dizziness;
- mental disorders with no known cause (stress, neuroses, depression);
- Flatulence;
- Symptoms of bowel disease;
- Change in body weight (both overweight and thinness);
- the simultaneous course of several diseases (or the succession of one disease to another);
- Cramping or pulling pain in the abdomen;
- Anemia;
- Retardation of physical and mental development in children;
- child hyperactivity or lethargy;
- enlarged lymph nodes (often in the acute stage of helminthiasis).
When to see a doctor
An infectious disease therapist or specialist deals with the treatment of parasitic diseases. If one or more of the above symptoms occur, a doctor should be consulted. Due to a rather sophisticated system of masking worms, you should explain the symptoms to the doctor as precisely as possible and also talk about your lifestyle: what food do you prefer, whether you have recently traveled and where, are there pets, etc.
Diagnosis of the disease
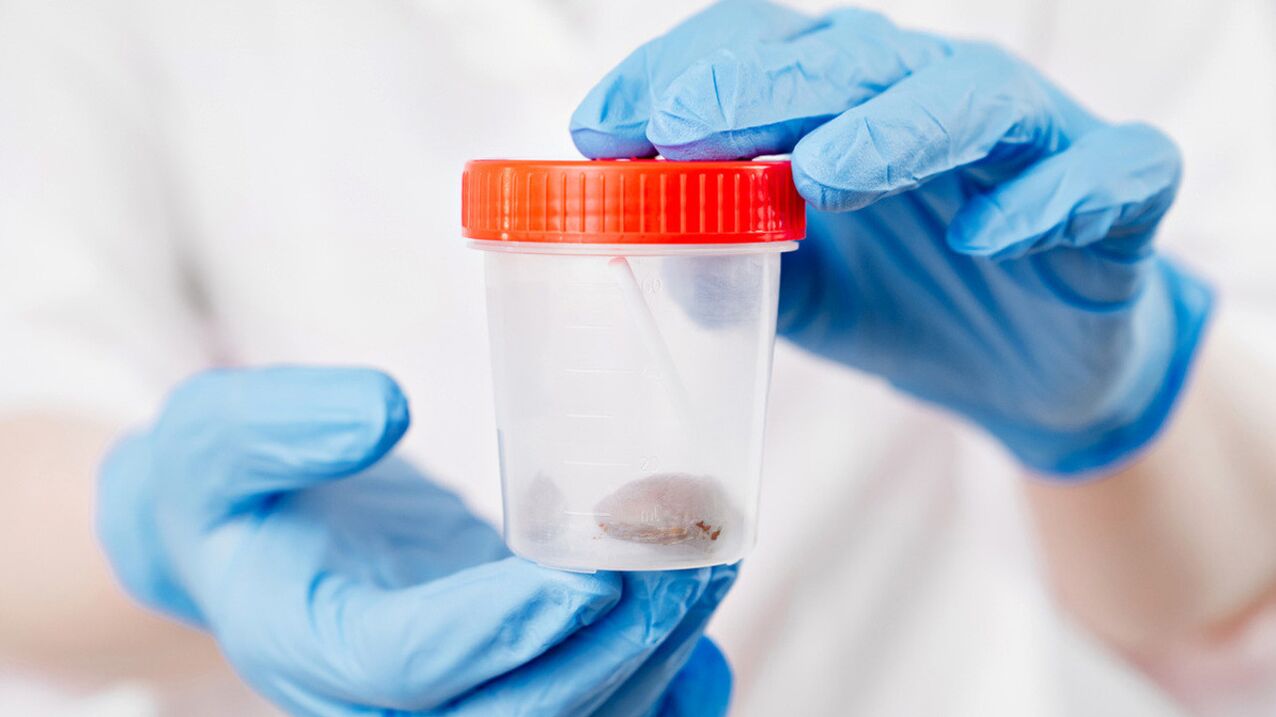
If the doctor suspects a helminth invasion, it's not difficult to identify. The following diagnostic methods are used for this:
- Stool examination. A fecal sample is given to the laboratory. They can contain eggs or larvae of parasites that live in the intestines.
- Scraping for enterobiasis. A swab is removed from the anus with a cotton swab. With this analysis, pinworms can be identified. The scraping should be done in the early morning before going to the bathroom.
- A blood test for antibodies. This is a pretty informative test that will help you identify a lot of parasites. However, even with a positive result, there is no one hundred percent guarantee that the parasites are still in the patient's body, because antibodies are retained even after they have been eliminated.
- Instrumental diagnostics. The use of radiography, MRI and CT with the use of contrast agents. These diagnostic methods make it possible to identify both large worms and some pathological changes in tissues caused by helminthic invasion.
As a rule, the doctor prescribes various studies to increase the reliability of the data obtained. Sometimes a patient needs to be tested multiple times to make an accurate diagnosis.
Important!When confirming helminthiasis, it is necessary to inform other close family members about it. An examination is recommended for them too. If the test is positive, it is important that all infected family members are treated. Otherwise, the eggs of the parasite will get back into the body of the recovered person and everything will have to be repeated from the beginning.
Treatment of helminths in children and adults
Despite the abundance of antiparasitic drugs in pharmacies, you cannot take them yourself. The doctor prescribes comprehensive treatment, trying not only to remove parasites, but also to get rid of the consequences of their vital activity.
As a rule, in addition to anthelmintics, the patient is prescribed vitamins and other drugs that eliminate the symptoms of the disease. The doctor selects medication for each patient separately, as each patient's symptoms are different.
Drugs used to treat helminthiasis
With helminthic invasions, patients are prescribed a complex of the following drugs:
- Anthelmintic medicines. These are anthelmintic drugs that either remove or kill worms. These goals are achieved by disrupting the parasites' metabolism or paralyzing their muscles. In the latter case, they lose their ability to stay in the intestine and are eliminated.
- Antihistamines. If the patient is allergic to parasites, doctors will prescribe antiallergic drugs at the time of treatment. This is extremely important, because when worms are killed in mass, a large number of allergens are released, which can provoke a strong allergic reaction. Antihistamines block the production of histamine, the main mediator of an allergic reaction.
- Enterosorbents. These are drugs that can bind substances in the gastrointestinal tract. In the treatment of worms, enterosorbents are used to bind and remove toxins excreted by the worms.
- Vitamins and minerals. Most often, B vitamins (folic acid and B12) and iron supplements are prescribed. This is necessary to treat anemia.
- Hepatoprotectors. These are drugs that protect the liver from toxic substances. These include preparations based on essential phospholipids or plant materials (milk thistle, artichoke, liquorice, St. John's wort and other plants).
- Probiotics and prebiotics. Prescribed to restore the intestinal microflora. Probiotics are live cultures of beneficial bacteria. Prebiotics are indigestible food components (like fiber) that are only fermented by the intestinal flora.
surgery
In most cases, it is enough to drink a drug complex. However, sometimes doctors are still forced to resort to surgery. For example, a large build-up of roundworms can cause an obstruction in the intestines. This is an urgent condition that requires surgery.
In the bile duct, worms can accumulate, against the background of which obstructive jaundice and even a liver abscess can develop. The same situation can occur in the pancreas and lead to acute pancreatitis. When the worms enter the appendix, appendicitis develops. All of these conditions require immediate surgery.
Surgery is often resorted to when organs are damaged by echinococci. These parasites accumulate and form echinococcal plugs in the liver, lungs, bones, kidneys, and even the brain. The danger of such a plug is that it can fester and burst.
Folk remedies for worms
Folk remedies for worms are not as effective as anthelmintics. This is just an auxiliary method - the main treatment is prescribed by a doctor.
Folk remedies are pumpkin seeds that contain cucurbitin, a substance that has an antihelminthic effect.
Myth 2: Garlic enemas get rid of worms
Worms really don't like garlic because it contains phytoncides - antibacterial and anti-parasitic substances. However, it is not necessary to do garlic enemas for helminthiasis. There are very few worms in the colon where the enema contents are injected. Most parasites live in the small intestine, so this procedure is useless. In addition, with such an enema, you can get serious irritation of the mucous membrane.
Prevention and Precautions

In most cases, the prognosis for the treatment of helminthiasis is favorable. Timely visit to the doctor avoids a number of complications that worms lead to.
Prevention of worms is reduced to compliance with the following recommendations:
- Wash your hands with soap and water before eating, after returning from the street, when using the toilet, or after contact with animals.
- Wash vegetables, fruits and herbs thoroughly. It is better to pour boiling water over them.
- Do not use other people's toiletries and dishes.
- Give up bad habits (smoking, alcohol).
- Avoid stress, it will have a positive effect on immunity.
- Show your pet to the vet regularly and vaccinate them in a timely manner.
- Undergo a comprehensive health check-up, including tests for worm eggs, each year.
- Cook meat, poultry, fish and eggs accordingly.
Myth 3: Parasites die in frozen meat.
This only applies to some worms. For example, the beef tapeworm really dies when the meat is frozen (minus 12 and below). And, for example, Trichinella larvae can only be eliminated after 2-3 hours of cooking.
diploma
The main cause of helminth invasions is poor hygiene. Improving hygiene and properly cooking pet food will greatly reduce the likelihood of helminthiasis. In most cases, worms do not pose a threat to human health if they are detected in a timely manner. But the lack of treatment still leads to serious consequences - anemia, damage to the nervous system and other infections.








































